- there are two versions of TCP/IP, IPv4 and IPv6.
- 10BASE-2 (Thinwire coaxial cable with a maximum segment length of 185 meters)
- 10BASE-5 (Thickwire coaxial cable with a maximum segment length of 500 meters)
- 10BASE-F (optical fiber cable)
- 10BASE-T (ordinary telephone twisted pair wire)
- 10BASE-36 (broadband multi-channel coaxial cable with a maximum segment length of 3,600 meters)
the video above shows how TCP/IP works.
hey guys, let's watch this amazing video about the difference between ipv4 and ipv6.
What is Ethernet (802.3)?
802.3 is a standard specification for Ethernet, a method of physical communication in a local area network (LAN), which is maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). In general, 802.3 specifies the physical media and the working characteristics of Ethernet. The original Ethernet supports a data rate of 10 megabits per second (Mbps) and specifies these possible physical media:
the video above explain the details about Wifi 802.11
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n
- 802.11a:
Operates in the 5.15GHz to 5.35GHz radio spectrum.
Speed: Up to 54Mbps (actual throughput is closer to 22Mbps)
Range: 50 feet
Less prone to interference.
More expensive.
Because 802.11b and 802.11a use different radio technologies and portions of the spectrum, they are incompatible with one another.
- 802.11b:
Operates in the 2.4GHz radio spectrum.
Speed: Up to 11Mbps
Range: 100 feet
Prone to interference (it shares airspace with cell phones, Bluetooth, security radios, and other devices).
Least expensive wireless LAN specification.
The Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA) has done its part by certifying hundreds of products to make sure they work together.
- 802.11g:
Operates in the 2.4GHz radio spectrum.
Speed: Up to 54Mbps
Range: 100 feet
Prone to interference (it shares airspace with cell phones, Bluetooth, security radios, and other devices).
- 802.11n (Draft):
Operates in the 2.4 or 5GHz radio spectrum
Speed: Up to 700Mbs
Range: 50 feet
Because 802.11b and 802.11g use the same radio technologies and portions of the spectrum, they are compatible with one another. But because the 802.11n standard has yet to be ratified by WECA, it may not be completely compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g.
How does a bluetooth connection work?
A Bluetooth device uses radio waves instead of wires or cables to connect to a phone or computer. A Bluetooth product, like a headset or watch, contains a tiny computer chip with a Bluetooth radio and software that makes it easy to connect. When two Bluetooth devices want to talk to each other, they need to pair.
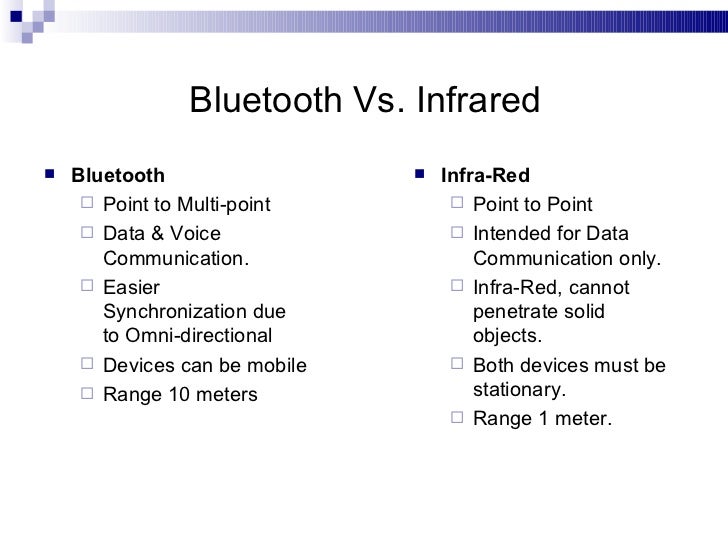
Bluetooth vs Infrared
Types of connection :
1) Dial-up connection
2) Direct connection
INTERNET INFRASTRCTURE

Source : http://seri06.blogspot.my/2013/05/the-internets-infrastructure.html
example of IP Address

USING THE NETWORK
1. company

2. individual
